A Bill of Materials (BOM) serves as a fundamental document in manufacturing, detailing all the materials, components, and parts required to construct or repair a product. It includes crucial information such as quantities, descriptions, costs, and procurement instructions. BOMs are essential for various manufacturing and supply chain processes, including production planning, inventory management, and cost estimation.

Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding and utilizing BOMs:
What is a Bill of Materials (BOM)?
A BOM is a structured list that identifies all the materials, components, and parts necessary for manufacturing or repairing a product. It acts as a blueprint for the manufacturing process, providing detailed instructions for procuring and using materials. BOMs are crucial for planning purchases, estimating costs, controlling inventory, and minimizing production delays and waste.
Key Elements of a Bill of Materials (BOM):
- BOM Level: This number acts like a map, pinpointing the exact location of each part or assembly within the overall structure of the BOM. It reveals whether a component is a fundamental element, a subassembly within a larger assembly, and so on, providing a clear understanding of its place in the product’s hierarchy.
- Part Number: Assigning a unique identifier to each material or component is crucial for efficient tracking and management. This unique code allows everyone involved, from designers to procurement specialists, to quickly and accurately pinpoint the specific item needed.
- Part Name: Alongside the part number, each component also requires a unique and descriptive name. This name should be clear and concise, easily distinguishing the part from others and aiding in identification during various stages of the product life cycle.
- Description: Beyond the name, a detailed description adds another layer of clarity. This description should provide sufficient information to eliminate any confusion about the specific characteristics, functionalities, or specifications of each part or assembly.
- Quantity: This element specifies the exact number of each individual part or assembly needed to complete the final product. Ensuring the accuracy of the quantity is crucial for avoiding production delays, material shortages, or unnecessary inventory buildup.
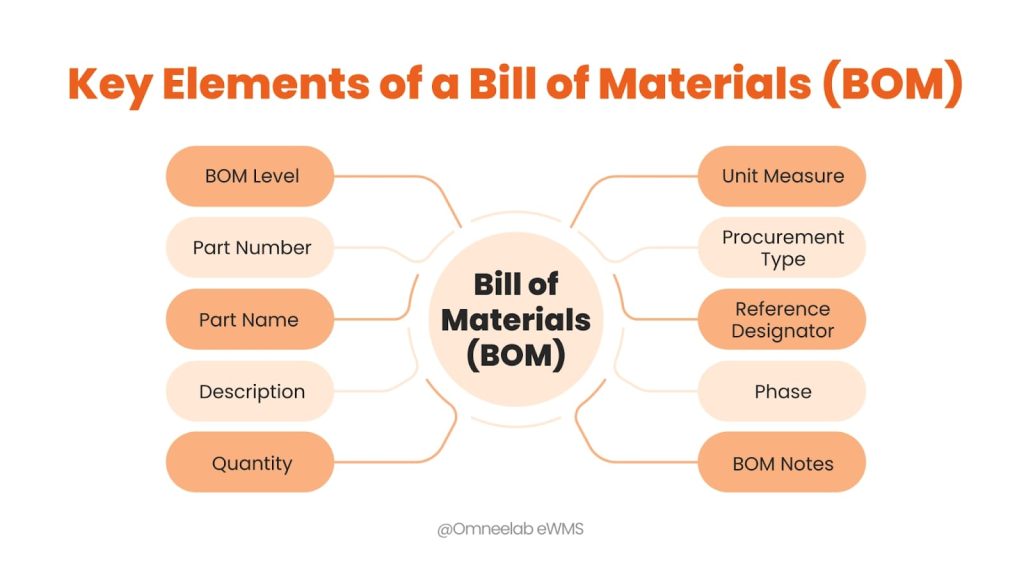
- Unit Measure: TSpecifying the unit of measurement for each part (e.g., each, meter, kilogram) ensures clear communication and avoids any confusion or miscalculations during the ordering, manufacturing, or assembly processes.
- Procurement Type: This element outlines the method for obtaining each part. Whether it’s purchased from a vendor, produced in-house, or outsourced through subcontracting, knowing the procurement type aids in efficient planning, cost estimation, and inventory management.
- Reference Designator: Particularly relevant in electronics, a reference designator acts as a unique identifier for each part’s specific location within an assembly. This allows for easy identification and placement during the manufacturing process.
- Phase: Tracking the lifecycle stage of each part, whether it’s “in production,” “in design,” or “obsolete,” provides valuable insights. This information helps with planning, forecasting, and ensuring the use of up-to-date components in the final product.
- BOM Notes: This section serves as an additional information hub, allowing users to include any relevant details not captured in the other elements. This could include information on alternative suppliers, special handling instructions, or specific technical specifications.
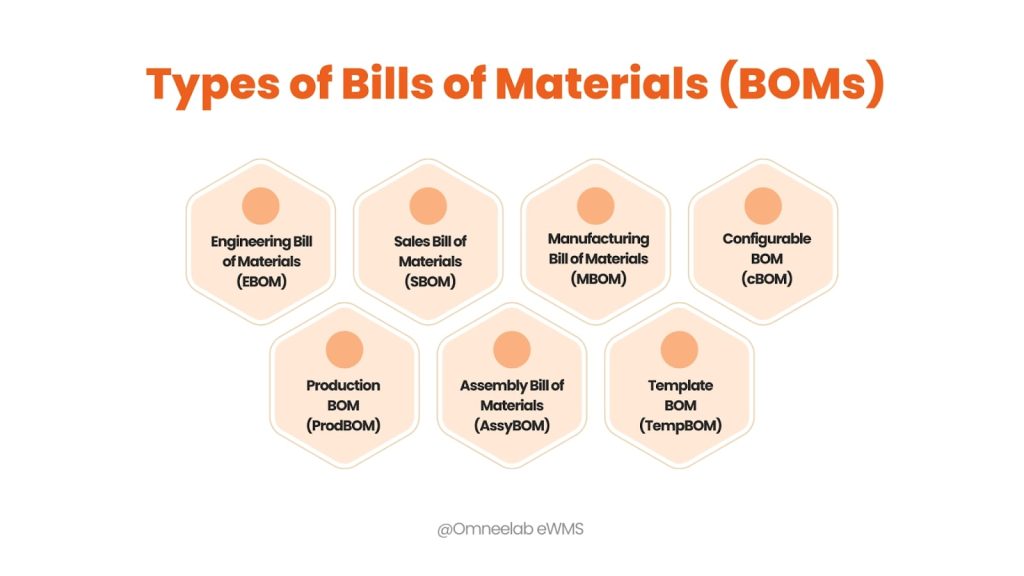
Types of Bills of Materials (BOMs):
- Engineering Bill of Materials (EBOM): This serves as the blueprint, capturing the product’s design intent as envisioned by the engineering team. It includes all components and subassemblies, regardless of manufacturability, focusing on functionality and performance. Think of it as the recipe used by the engineers to define the product’s essence.
- Sales Bill of Materials (SBOM):This acts as a customer-centric view, listing the products and components required to fulfill specific customer orders. It may differ from other BOMs by excluding internal components not directly relevant to the final product delivered to the customer. This provides a clear picture of what goes into each unique customer order.
- Manufacturing Bill of Materials (MBOM): This plays a central role on the production floor, meticulously detailing all parts and assemblies needed to produce the finished product physically. It takes into account manufacturing constraints, lead times, and potential substitutions, ensuring a smooth and efficient production process.
- Configurable BOM (cBOM): This caters to products that can be customized based on individual customer needs. It allows for the inclusion of various options and alternative components, providing flexibility in building products to specific customer configurations. This caters to the ever-evolving needs of today’s dynamic market.
- Production BOM (ProdBOM): This serves as the backbone for production orders, acting as the official list of components needed to manufacture specific quantities of the product. It ensures that all necessary parts are available in the right quantities at the right time, minimizing production delays and ensuring efficient resource allocation.
- Assembly Bill of Materials (AssyBOM): This focuses on the hierarchical structure of assemblies, listing both the parent assembly and its constituent subassemblies. This information is crucial for sales purposes, allowing for accurate pricing, quoting, and understanding of the complete product offering.
- Template BOM: This offers a flexible structure, adaptable for both production and sales scenarios. It can be customized to include various elements relevant to each specific use case, providing a versatile tool for different departments within an organization.
Advantages of a BOM:
- Ensures availability of materials and components during production: By listing all necessary parts and their quantities, a BOM allows for accurate planning and procurement. This avoids production delays caused by missing materials, keeping the assembly line running smoothly.
- Maintains consistency and uniformity in product assembly: A BOM serves as a blueprint for assembly, specifying the exact components and their correct assembly order. This ensures that every product is built the same way, meeting consistent quality standards and reducing the risk of errors or variations.
- Facilitates tracking of product failures and identification of faulty components: When a product malfunctions, the BOM allows for efficient troubleshooting. By tracing the used components back to the BOM, technicians can quickly pinpoint potential culprits, saving time and resources during the repair process.
- Helps in cost estimation, inventory control, and production planning: By providing a detailed breakdown of components and their costs, the BOM enables accurate cost estimation for the entire product. Additionally, it helps in maintaining optimal inventory levels by identifying the required quantities of each item and preventing overstocking or understocking. This information also facilitates efficient production planning, allowing for resource allocation and scheduling based on material needs.
Creation of Bill of Materials (BOM):
- Identify Essential Data: Before diving in, determine the crucial information each BOM entry needs to encompass. This typically includes item number, part name, description, quantity per assembly, unit of measure, and potential supplier information.
- Establish Centralized Control: Assign a designated individual or team responsibility for maintaining and updating the BOM. This ensures consistency and prevents conflicting information from circulating.
- Limit Editing Access & Track Revisions: Implement restrictions on who can edit the BOM, minimizing the risk of unauthorized changes. Additionally, track all revisions made, including the date, author, and reason for the modification, allowing for easy reference and rollback if necessary.
- Select the Right Structure: Decide whether a single-level BOM, listing all components directly, or a multi-level BOM, showcasing assemblies within assemblies, is more appropriate for your product’s complexity.
- List Components with Precision:Meticulously list all materials, components, and parts required for production. Ensure clarity and accuracy in descriptions to avoid confusion or delays during assembly.
- Continuously Refine the List: As your product evolves or sourcing strategies change, the BOM should reflect these updates. Regularly review and update the list to maintain its effectiveness.
- Maintain Revision History: Track all changes made to the BOM. This allows for tracing modifications, reverting to previous versions if necessary, and ensuring everyone involved is working with the most current information.
History of the Bill of Materials:
- Automated Creation and Management: WMS software can streamline the BOM creation process by automatically generating a BOM from product information and assembly instructions. This eliminates manual tasks, reduces errors, and saves valuable time.
- Enhanced Change Tracking: WMS systems ensure accurate and timely updates to BOMs. Whenever changes occur, like revisions or substitutions, the system automatically reflects them, preventing version control issues and discrepancies. This transparency allows everyone involved to work with the most up-to-date information.
- Optimized Inventory Management and Supply Chain Resilience: WMS software leverages BOM data to optimize inventory levels for each component needed in production. This helps minimize overstocking and ensures essential materials are readily available. Additionally, by providing real-time insights into component availability, WMS allows for proactive adjustments to supply chain strategies, increasing resilience in the face of disruptions.
Leveraging BOM Power with WMS Systems:
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) elevate the effectiveness of BOMs by offering several key benefits:
- Early 20th Century Roots: The concept of a bill of materials (BOM) emerged within the field of materials management during the early 1900s. This initial iteration likely involved manual lists or rudimentary documents outlining the components needed for production.
- Evolving Alongside Production Techniques: Throughout the mid-20th century, the BOM evolved alongside advancements in production planning and materials management strategies. It became intertwined with the development of Materials Requirements Planning (MRP) in the 1960s, playing a crucial role in streamlining inventory management and production scheduling.
- Integration with Enterprise Systems: The arrival of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems in the latter half of the 20th century further expanded the role of the BOM. It became integrated with these comprehensive software solutions, allowing for centralized control and streamlined communication across various departments within an organization.
- Modern Cornerstone: Today, the BOM remains an indispensable tool within modern manufacturing and supply chain management. It serves as a critical data source for various functions, including cost estimation, inventory control, production planning, and efficiently managing complex assemblies.
In summary, a well-structured and accurate BOM is the cornerstone of efficient manufacturing. Streamline production, reduce costs, and ensure quality with Omneelab WMS, the comprehensive BOM management solution.
People also read:
- Small Business Barcoding
- Demand-driven Replenishment Practices for Retailers
- Guide to Managing Perishable Inventory
- Inventory Management with Barcode Technology
- Common Inventory Management Challenges
- Comprehensive Guide to Inventory Management Systems
- Manual and Automated Inventory Management
- Top 10 Tips for Warehouse Management Software

Kapil Pathak is a Senior Digital Marketing Executive with over four years of experience specializing in the logistics and supply chain industry. His expertise spans digital strategy, search engine optimization (SEO), search engine marketing (SEM), and multi-channel campaign management. He has a proven track record of developing initiatives that increase brand visibility, generate qualified leads, and drive growth for D2C & B2B technology companies.