Have you ever wondered why some businesses consistently meet customer demands while others struggle with stockouts and delayed deliveries? The answer often lies in their understanding and management of lead time. In today’s fast-paced business environment, mastering lead time in inventory management isn’t just beneficial—it’s essential for survival and growth.

Lead time represents the total duration between placing an order and receiving the goods in your inventory. This critical metric affects everything from customer satisfaction to cash flow, making it one of the most important concepts in inventory management. Whether you’re a small business owner or managing a large enterprise, understanding lead time can transform your operations and give you a competitive edge.
According to recent supply chain research, companies that effectively manage their lead times experience 15% higher customer satisfaction rates and 23% lower inventory carrying costs compared to those with poor lead time control In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about lead time meaning, from basic definitions to advanced optimization strategies. You’ll discover how to calculate lead time accurately, identify factors that influence it, and implement proven techniques to minimize delays and maximize efficiency.
What is Lead Time in Inventory Management?
Lead Time Definition
Lead time meaning in inventory management refers to the total time elapsed from the moment you place a purchase order until the products arrive at your facility and are ready for use or sale. This timeframe encompasses multiple stages of the procurement and delivery process, making it a crucial factor in inventory planning and stock management.
To define lead time more precisely, it includes:
- Order processing time
- Manufacturing lead time (if applicable)
- Transit time and shipping
- Receiving and inspection procedures
- Quality control processes
Types of Lead Time
Understanding the different types of lead time helps businesses identify bottlenecks and optimize their supply chain operations:
1. Procurement Lead Time This covers the time from placing an order with your supplier until the goods arrive at your warehouse. Procurement lead time varies significantly based on supplier location, product complexity, and shipping methods.
2. Manufacturing Lead Time For businesses that produce goods, manufacturing lead time includes the time required to convert raw materials into finished products. This encompasses production scheduling, processing time, and quality control.
3. Customer Lead Time Also known as order fulfillment time, this represents the time customers wait from placing an order until receiving their products. Minimizing customer lead time is crucial for maintaining high service levels.
4. Cumulative Lead Time This comprehensive metric includes all lead times in your supply chain, from raw material procurement to final product delivery.
How to Calculate Lead Time in Inventory Management
Basic Lead Time Formula
The fundamental lead time formula is straightforward:
Lead Time = Order Date – Receipt Date
However, for more accurate lead time calculation, consider this expanded formula:
Total Lead Time = Order Processing Time + Production Time + Transit Time + Receiving Time
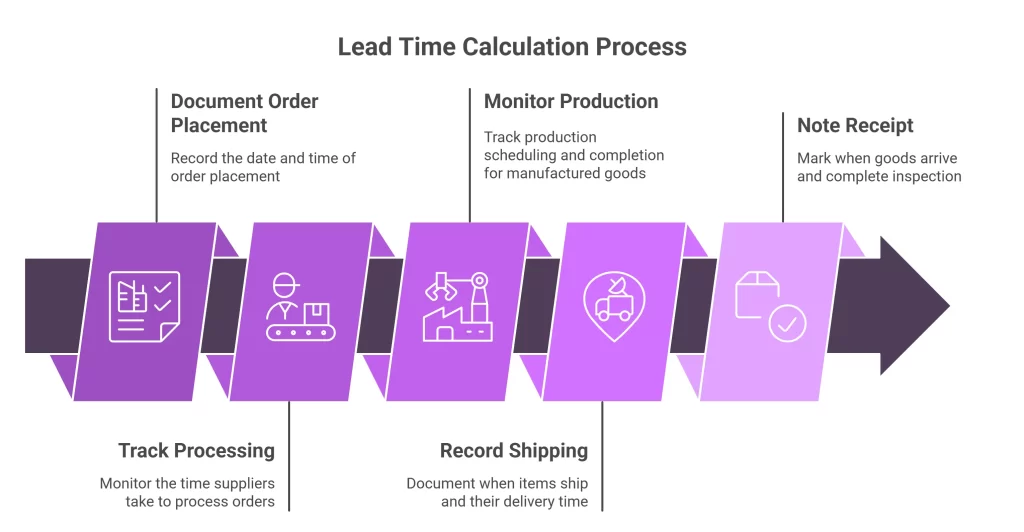
Step-by-Step Lead Time Calculation
- Document Order Placement: Record the exact date and time when you place each order
- Track Processing: Monitor how long suppliers take to process your orders
- Monitor Production: For manufactured goods, track production scheduling and completion
- Record Shipping: Document when items ship and their delivery time
- Note Receipt: Mark when goods arrive and complete inspection
Practical Example
Let’s say you order office supplies:
- Order placed: January 1st
- Supplier processes order: 2 days
- Manufacturing lead time: 5 days
- Shipping and transit time: 3 days
- Receiving and inspection: 1 day
Total Lead Time = 2 + 5 + 3 + 1 = 11 days
Factors Affecting Lead Time
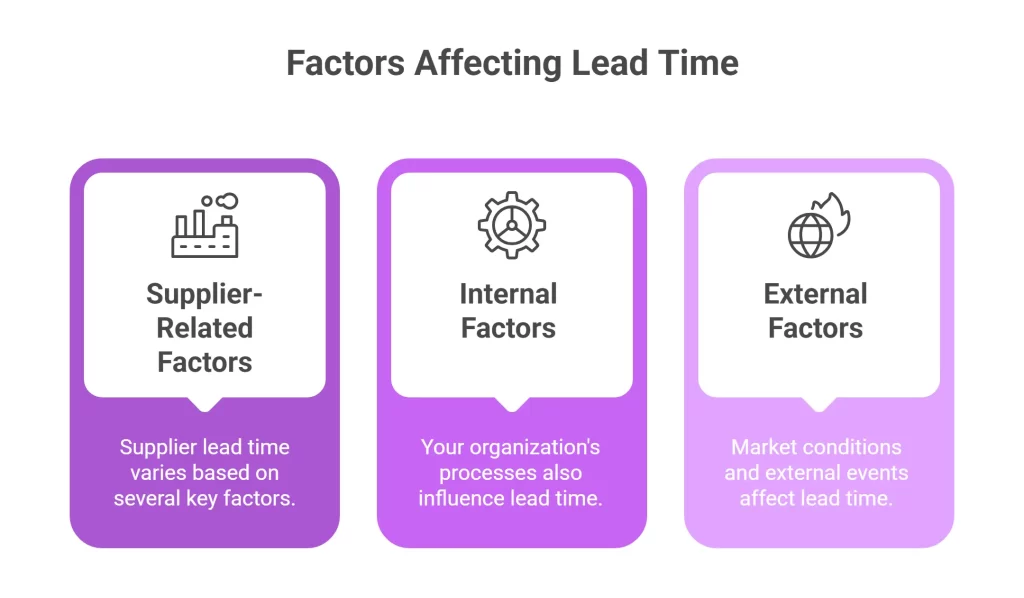
Supplier-Related Factors
Supplier lead time varies based on several key factors:
- Geographic location: Distance affects transit time
- Production capacity: Supplier workload impacts processing time
- Technology and automation: Advanced systems reduce cycle time
- Quality control processes: Thorough inspection may increase waiting time
Internal Factors
Your organization’s processes also influence lead time:
- Order processing efficiency: Streamlined systems reduce delays
- Communication quality: Clear specifications prevent rework
- Payment terms: Faster payments may prioritize your orders
- Relationship strength: Long-term partnerships often yield better service
External Factors
Market conditions and external events affect lead time:
- Seasonal demand fluctuations: Peak seasons increase lead times
- Economic conditions: Market volatility impacts supplier performance
- Transportation infrastructure: Road conditions and logistics capabilities
- Regulatory requirements: Compliance checks may extend timelines
Lead Time Management Strategies
Demand Forecasting Integration
Effective demand forecasting helps predict future needs and plan orders accordingly. By analyzing historical data and market trends, you can:
- Anticipate demand spikes
- Adjust order quantities and timing
- Reduce reliance on expedited shipping
- Improve inventory turnover ratio
Supplier Relationship Management
Building strong supplier relationships is crucial for lead time optimization:
- Negotiate better terms: Long-term contracts often yield priority treatment
- Implement vendor managed inventory: Let suppliers monitor and replenish stock
- Establish backup suppliers: Multiple sources reduce dependency risks
- Regular performance reviews: Monitor and improve supplier performance
Technology Solutions
Modern inventory management systems offer powerful tools for lead time management:
- Automated reorder points calculation: Trigger orders when stock reaches predetermined levels
- Real-time tracking: Monitor orders throughout the supply chain
- Predictive analytics: Forecast lead time variations
- Integration capabilities: Connect with supplier systems for seamless communication
Lead Time and Safety Stock Relationship
Understanding Safety Stock
Safety stock serves as a buffer against lead time variability and demand uncertainty. The relationship between lead time and safety stock is fundamental to effective inventory control:
Safety Stock = (Maximum Lead Time – Average Lead Time) × Average Daily Usage
Industry data shows that businesses maintaining optimal safety stock levels reduce stockout incidents by 40% while keeping inventory costs within acceptable ranges Understanding what is buffer stock and its relationship to lead time is crucial for maintaining optimal inventory levels while minimizing carrying costs.
Buffer Stock Calculation
Buffer stock helps maintain service levels during lead time delays:
- Calculate lead time variability: Measure standard deviation of historical lead times
- Determine service level targets: Decide acceptable stockout risk (typically 95-99%)
- Apply safety stock formula: Use statistical methods to calculate optimal buffer levels
- Monitor and adjust: Regularly review and update safety stock levels
Balancing Act
The key is finding the optimal balance between:
- Carrying costs: Excess inventory ties up capital
- Service levels: Stockouts damage customer relationships
- Lead time uncertainty: Variability requires additional buffer stock
Lead Time Optimization Techniques
Lean Manufacturing Principles
Implementing just in time inventory principles can significantly reduce lead times:
- Eliminate waste: Remove non-value-adding activities
- Streamline processes: Optimize workflow and reduce cycle time
- Improve quality: Reduce rework and inspection time
- Enhance communication: Faster information flow accelerates decisions
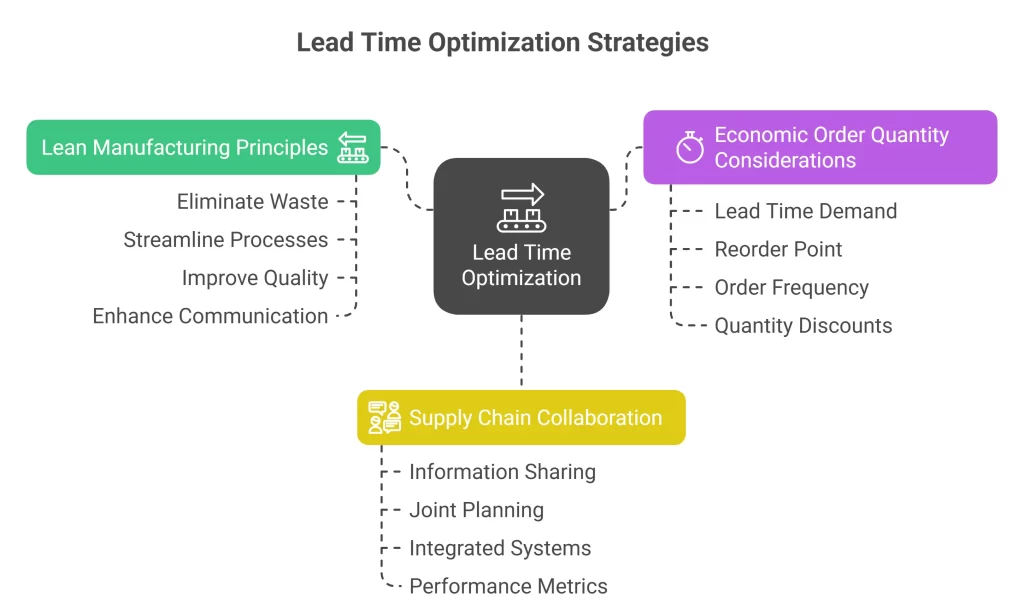
Economic Order Quantity Considerations
Economic order quantity (EOQ) calculations should incorporate lead time factors:
- Lead time demand: Calculate consumption during inventory replenishment period
- Reorder point: Set trigger levels considering lead time and safety stock
- Order frequency: Balance ordering costs with carrying costs
- Quantity discounts: Evaluate bulk purchase benefits against extended lead times
Supply Chain Collaboration
Collaborative approaches can dramatically improve lead time performance:
- Information sharing: Provide suppliers with demand forecasts
- Joint planning: Coordinate production schedules with suppliers
- Integrated systems: Connect IT systems for real-time visibility
- Performance metrics: Establish shared KPIs and improvement targets
Industry-Specific Lead Time Considerations
Construction Industry
Construction inventory management faces unique lead time inventory challenges:
- Project-based demand: Irregular ordering patterns
- Seasonal constraints: Weather affects delivery schedules
- Site logistics: Delivery coordination complexity
- Specialized materials: Longer lead times for custom components
Healthcare and Medical
Medical inventory management requires careful lead time planning:
- Regulatory compliance: Additional inspection and approval time
- Product shelf life: Expiration dates limit inventory holding periods
- Critical supplies: Zero tolerance for stockouts on essential items
- Temperature control: Special handling requirements may extend lead times
Restaurant Industry
Restaurant inventory management involves perishable goods with short lead times:
- Fresh ingredients: Daily or weekly delivery requirements
- Menu planning: Coordinating lead times with meal preparation
- Seasonal availability: Ingredient availability affects lead times
- Local sourcing: Shorter lead times but limited supplier options
Lead Time Metrics and KPIs
Key Performance Indicators
Monitor these essential lead time KPIs:
- Average lead time: Overall performance baseline
- Lead time variability: Consistency measurement
- On-time delivery rate: Supplier reliability metric
- Lead time accuracy: Forecast vs. actual comparison
Benchmarking and Analysis
Regular lead time analysis helps identify improvement opportunities:
- Historical trending: Track lead time changes over time
- Supplier comparison: Evaluate relative performance
- Product category analysis: Identify patterns by item type
- Seasonal adjustments: Account for cyclical variations
Continuous Improvement
Implement ongoing improvement processes:
- Root cause analysis: Investigate lead time delays
- Process mapping: Visualize and optimize workflows
- Feedback loops: Gather input from suppliers and customers
- Regular reviews: Schedule periodic performance assessments
Technology and Lead Time Management
Inventory Management Software
Modern inventory management software provides powerful lead time management capabilities:
- Automated calculations: Real-time lead time tracking
- Predictive analytics: Forecast future lead time trends
- Alert systems: Notify stakeholders of potential delays
- Integration features: Connect with supplier and customer systems
RFID and Barcode Technology
RFID Asset tracking technologies improve lead time visibility:
- Real-time location tracking: Monitor shipments in transit
- Automated data capture: Reduce manual entry errors
- Inventory accuracy: Improve stock level precision
- Process efficiency: Streamline receiving and inspection
AI and Machine Learning
Digital transformation in supply chain management is accelerating rapidly. Research indicates that companies implementing AI-powered inventory systems see an average 18% reduction in lead times and 25% improvement in forecast accuracy Emerging technologies are revolutionizing lead time management:
- Demand prediction: More accurate forecasting
- Supplier performance modeling: Predict delivery reliability
- Route optimization: Reduce transit time
- Anomaly detection: Identify potential delays early
Common Lead Time Challenges and Solutions
Challenge 1: Inconsistent Supplier Performance
Solution: Implement supplier scorecards and regular performance reviews. Establish clear expectations and consequences for poor performance.
Challenge 2: Inaccurate Lead Time Estimates
Solution: Use historical data and statistical analysis to improve forecasting accuracy. Regularly update lead time estimates based on recent performance.
Challenge 3: Communication Gaps
Solution: Establish standardized communication protocols and use integrated systems for real-time information sharing.
Challenge 4: Seasonal Variations
Solution: Develop seasonal lead time models and adjust safety stock levels accordingly. Plan ahead for known peak periods.
Best Practices for Lead Time Management
Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintain comprehensive records of:
- Order history: Track all purchase orders and receipts
- Supplier performance: Document delivery times and quality issues
- Process improvements: Record changes and their impacts
- Exception reports: Analyze delays and their causes
Communication Protocols
Establish clear communication standards:
- Regular updates: Schedule periodic supplier check-ins
- Escalation procedures: Define when and how to address delays
- Information sharing: Provide suppliers with relevant demand data
- Feedback mechanisms: Create channels for continuous improvement
Training and Development
Invest in team capabilities:
- Process training: Ensure staff understand lead time concepts
- Technology skills: Train users on inventory management systems
- Supplier management: Develop relationship management skills
- Problem-solving: Build analytical and troubleshooting capabilities
Future Trends in Lead Time Management
Digital Transformation
The future of lead time management includes:
- IoT integration: Connected devices providing real-time data
- Blockchain technology: Enhanced supply chain transparency
- Cloud-based solutions: Improved accessibility and scalability
- Mobile applications: On-the-go inventory management
Sustainability Considerations
Environmental factors increasingly influence lead time decisions:
- Local sourcing: Reduced transit time and carbon footprint
- Green logistics: Sustainable transportation options
- Circular economy: Recycling and reuse affecting supply chains
- Regulatory compliance: Environmental regulations impacting processes
Conclusion
Mastering lead time in inventory management is crucial for business success in today’s competitive marketplace. By understanding the components of lead time, implementing effective calculation methods, and applying proven optimization strategies, you can significantly improve your operations.
Remember these key takeaways:
- Lead time directly impacts customer satisfaction and cash flow
- Accurate lead time calculation requires comprehensive data collection
- Safety stock and buffer stock help manage lead time variability
- Technology solutions can dramatically improve lead time visibility and control
- Continuous improvement and supplier collaboration are essential for optimization
Ready to transform your inventory management? Start by implementing the lead time calculation methods discussed in this guide. Consider exploring advanced inventory management software solutions that can automate these processes and provide real-time insights into your supply chain performance. With proper lead time management, you’ll be well-positioned to meet customer demands, optimize costs, and drive business growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Lead time is the total time from order placement to receipt, while cycle time refers to the time required to complete one unit of production or one complete process cycle. Lead time includes all waiting periods and delays, whereas cycle time focuses on active processing time.
Longer lead times typically require higher safety stock levels, which can reduce your inventory turnover ratio. By optimizing lead times, you can maintain lower inventory levels while meeting customer demand, thereby improving your turnover ratio and cash flow.
Lead time variability measures the consistency of delivery times from suppliers. High variability requires larger buffer stock to maintain service levels, increasing carrying costs. Managing variability through supplier development and process improvement is crucial for efficient inventory management.
Businesses can reduce supplier lead time by: building strong partnerships, providing accurate demand forecasts, negotiating better terms, implementing vendor managed inventory, using local suppliers, and investing in supplier development programs.
Demand forecasting helps predict future inventory needs, allowing businesses to place orders with appropriate timing. Accurate forecasts enable better planning, reduce rush orders, and help optimize the balance between inventory holding costs and service levels during lead time periods.

Kapil Pathak is a Senior Digital Marketing Executive with over four years of experience specializing in the logistics and supply chain industry. His expertise spans digital strategy, search engine optimization (SEO), search engine marketing (SEM), and multi-channel campaign management. He has a proven track record of developing initiatives that increase brand visibility, generate qualified leads, and drive growth for D2C & B2B technology companies.