In the vast world of global trade, warehouses stand as vital structures, silently managing the flow of products from manufacturing plants to the hands of consumers. These structures serve a pivotal purpose, acting as storage areas for goods and ensuring the seamless operation of the supply chain. But what exactly are warehouses, and why are they essential in the intricate dance of commerce?

Warehouses are specialized facilities designed to store, organize, and manage various goods and products. Imagine them as carefully structured repositories, properly arranged to accommodate a diverse range of items, from electronics to clothing, and from perishable goods to industrial equipment. Within these walls, products find a temporary home, awaiting their moment to be dispatched to retailers, wholesalers, or directly to consumers. The fundamental purpose of warehouses lies in their ability to bridge the gap between production and consumption. As products are manufactured, they need a secure place to reside until they are needed in the market. Warehouses provide this safe haven, ensuring that products are stored in optimal conditions, shielded from environmental factors and potential damage.
So, why are warehouses indispensable in the field of commerce? Their significance stems from several key factors. Firstly, they enable businesses to maintain a consistent supply of products. By stockpiling goods, companies can meet fluctuating consumer demands without interruptions, ensuring that popular items are readily available.
Moreover, warehouses play a crucial role in cost management. By allowing businesses to buy and store goods in bulk, warehouses enable economies of scale. Bulk purchasing often leads to lower unit costs, reducing the overall expenses for businesses. Additionally, warehouses offer a buffer against price fluctuations. When prices are favorable, companies can stock up, securing products at lower costs to meet future demands. In essence, warehouses serve as the linchpin in the supply chain, ensuring a harmonious balance between production and consumption. They provide businesses with the flexibility to manage inventory effectively, respond promptly to market demands, and optimize costs.
Understanding Warehouse Management
Warehouse management is far more than the mere storage of goods; it encompasses a wide array of processes that require careful organization and meticulous planning. At its core, warehouse management involves a large number of tasks aimed at organizing, controlling, and optimizing various facets of a warehouse’s functions. Let’s delve into the key elements that define effective warehouse management, exploring topics such as inventory control, order fulfillment, space utilization, and labor management.
Inventory Management Strategies
Maintaining an optimal balance in inventory levels is akin to walking a tightrope in the business world. Too much stock ties up valuable capital, leading to financial strain, while insufficient stock levels result in stock outs, dissatisfied customers, and missed business opportunities.
Inventory Management system is the secret sauce that keeps the gears of warehouse operations turning smoothly. It’s not just about counting products on shelves; it’s the strategic art and science of ensuring a business has the right amount of goods at the right time. Imagine it as a well-choreographed dance where products flow seamlessly from manufacturers to customers. This process is integral to Warehouse Management, ensuring that products are not only stored securely but also efficiently organized and dispatched with precision. As the demand for various products continues to rise, Inventory Management becomes a crucial element in warehouse operations, optimizing the balance between supply and demand, minimizing costs, and enhancing overall efficiency. In essence, Inventory Management tool that ensures the right products are in the right place at the right time, making warehouse management a symphony of seamless operations.
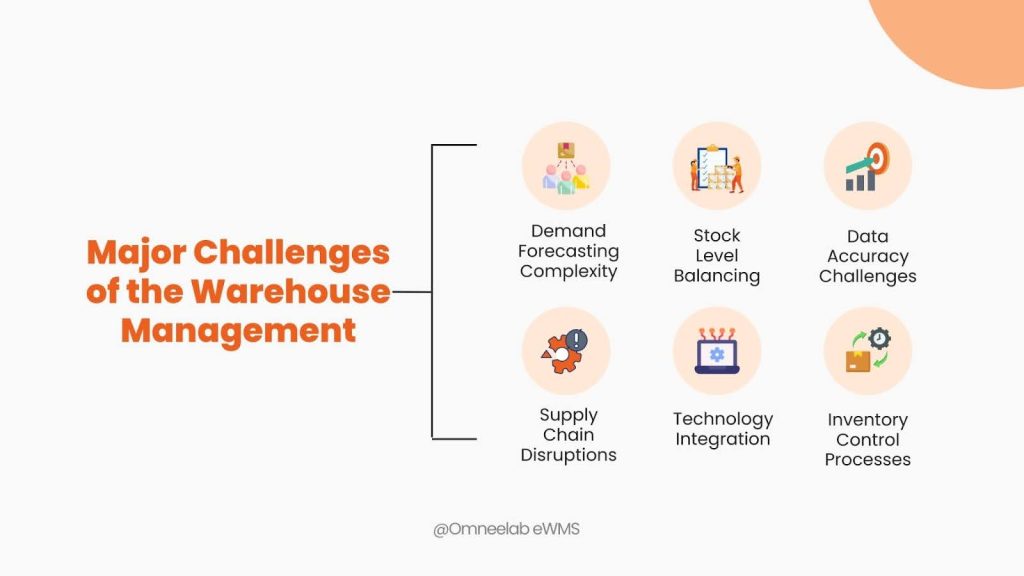
Challenges Faced Today in Warehouse Management
Demand Forecasting Complexity:
Accurate prediction of future demand is challenging due to factors like seasonal variations, market dynamics, and unforeseen events such as economic shifts or sudden changes in consumer behavior.
Stock Level Balancing:
Striking the right balance between overstocking and understocking is critical. Overstocking ties up capital in excess inventory, while understocking can result in lost sales, dissatisfied customers, and potential damage to the brand’s reputation.
Data Accuracy Challenges:
Maintaining accurate inventory records is an ongoing challenge. Manual errors in data entry, technical glitches in the inventory management system, and discrepancies between recorded and actual stock levels can all contribute to inaccuracies.
Supply Chain Disruptions:
External factors can impact the timely replenishment of goods. Natural disasters affecting production or transportation, political instability, and global events like pandemics can disrupt supply chains globally.
Technology Integration:
Leveraging advanced technology is essential for efficient inventory management. Implementation of data analytics for better forecasting, automation to streamline processes and reduce human error, and the use of RFID or barcoding systems for real-time tracking is crucial.
Inventory Control Processes:
Robust control processes are necessary for minimizing errors and optimizing Operations. Regular cycle counting and audits ensure accuracy, just-in-time inventory strategies help reduce holding costs, and periodic reviews and adjustments are made based on changing market conditions.
Prominent strategies used in the Industry
Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory Systems
The Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory system is a strategic approach that aims to optimize inventory levels by ensuring products arrive precisely when needed, minimizing excess stock. This methodology requires meticulous coordination with suppliers to deliver raw materials or finished products just in time for production or sale. By synchronizing the supply chain with consumer demand, businesses can reduce holding costs, minimize waste, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Implementing JIT inventory systems involves establishing robust relationships with suppliers, implementing advanced forecasting techniques, and investing in efficient transportation and logistics networks. By adopting JIT principles, businesses not only streamline their inventory management but also create a responsive supply chain capable of adapting swiftly to market fluctuations and consumer demands.
ABC Analysis
ABC analysis is a classification strategy that categorizes inventory into three groups – A, B, and C – based on their significance. Class A items, representing high-value goods, receive stricter control and attention, while Class C items, typically lower in value, have less stringent control. This strategy allows businesses to prioritize resources effectively, focusing on critical items to optimize inventory management. ABC analysis provides a structured approach to handling diverse products within the warehouse.
Bulk Shipments
For certain businesses, bulk shipments are a strategic approach to inventory management. This involves ordering and receiving inventory in large quantities, leveraging economies of scale in procurement. The implementation of bulk shipments requires accurate forecasting to determine optimal order quantities and storage capacity. The benefits include reduced shipping costs per unit and potential discounts from suppliers. While it requires careful planning, bulk shipments are instrumental in managing costs and ensuring a steady supply of goods.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a modern inventory strategy that minimizes the need for extensive warehousing. In this model, retailers fulfill customer orders by purchasing products directly from third-party suppliers, who then ship the products directly to customers. Dropshipping offers several advantages, including lower holding costs, a broader product range without extensive inventory, and reduced risks of overstock. This strategy is particularly beneficial for businesses aiming for flexibility and scalability
Prominent strategies used in the Industry
Within the dynamic environment of a warehouse, order fulfillment emerges as the heartbeat of operations. This critical process involves the accurate picking, packing, and shipping of products to fulfill customer orders. In the competitive landscape of modern commerce, precision in order fulfillment is paramount, directly influencing customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
And for order fulfillment to be excellent, every detail matters. From the strategic arrangement of products within the warehouse to the innovative methodologies employed, order fulfillment is an amalgamation of efficiency. The competitive edge in the contemporary market is not solely about the quality of products but equally about the seamlessness with which orders are processed and delivered.
As we read more about the intricacies of order fulfillment, we will learn about the various strategies and technologies that warehouses employ to optimize their order operations. From batch picking techniques that maximize efficiency to the organization of zone picking, and the strategic waves of order processing, each vertical give their contribution, ensuring a streamline flow to the entire process.
Batch Picking – Maximizing Efficiency through Grouped Orders
Batch picking is a strategic approach wherein multiple orders with similar products are grouped together for simultaneous picking, optimizing routes and minimizing travel time within the warehouse. This method significantly enhances operational efficiency, allowing warehouse staff to fulfill multiple orders in a single pass through the inventory, reducing the time and resources required for order fulfillment. By grouping similar items, batch picking minimizes the need for redundant movements, leading to substantial time savings and increased throughput.
Zone Picking – Navigating Warehouse Zones for Order Fulfillment
Zone picking involves dividing the warehouse into distinct zones, each assigned to specific products or product categories. When an order is received, designated pickers in each zone are responsible for selecting items within their assigned area. Once all items are picked, they are consolidated for packing and shipping. Zone picking optimizes workflow by reducing the distance traveled by pickers, minimizing congestion, and ensuring systematic organization within the warehouse. This approach enhances productivity by allowing specialized handling of products within each zone, leading to faster and more accurate order fulfillment.
Wave Picking – Organized Order Batching
Wave picking revolutionizes the order fulfillment process by organizing orders into waves, allowing for simultaneous picking, packing, and shipping of multiple orders. During peak demand periods, wave picking enables warehouse efficiency to handle a high volume of orders without compromising accuracy or speed. By strategically batching orders based on criteria such as destination, delivery urgency, or product type, wave picking minimizes idle time between picking and packing, ensuring a continuous workflow and optimizing resource utilization. This method enhances operational flexibility, enabling warehouses to adapt swiftly to fluctuating order volumes and dynamic market demands.
Space Utilization
In the realm of warehouse management, space is a precious commodity that must be utilized with utmost efficiency. The strategic organization of products within the warehouse directly impacts storage capacity, accessibility, and operational flow. To optimize space utilization, warehouses employ various techniques and storage solutions tailored to the specific characteristics of their inventory.
At its essence, warehouse space management involves the deliberate organization of products to make the most effective use of available space. This arrangement is not merely about fitting items onto shelves but rather a thoughtful consideration of how spatial dynamics impact the efficiency and functionality of the entire warehouse ecosystem. The importance of this effective arrangement cannot be overstated as in the ever-evolving landscape of modern commerce, where the demand for swift order fulfillment is constant, a well-organized and optimized warehouse space becomes a competitive advantage. It is the difference between a seamless, agile operation and one fraught with inefficiencies.
One of the primary benefits of meticulous space management is the maximization of storage capacity. By utilizing space vertically and employing strategic storage solutions, warehouses can accommodate a larger inventory without the need for expansive physical footprints. This not only enhances efficiency but also contributes to cost-effectiveness by avoiding unnecessary expansion costs.
Accessibility is another critical factor influenced by space management. A well-organized warehouse ensures that products are stored in a manner that facilitates easy retrieval. This directly impacts order fulfillment speed and minimizes the time and effort required to locate and retrieve specific items. The result is a streamlined process that enhances overall productivity. Moreover, an efficiently managed warehouse space contributes to a safer working environment. Clear pathways, organized storage areas, and a clutter-free space reduce the risk of accidents and improve the overall safety of warehouse operations. This is particularly crucial in environments where heavy machinery and equipment are in use.
Pallet Racks: Utilizing Vertical Space for Maximum Storage
Pallet racks are a fundamental component of warehouse storage, enabling the efficient use of vertical space. These racks consist of multiple shelves designed to accommodate pallets, optimizing storage by stacking products vertically. By utilizing the height of the warehouse, pallet racks significantly increase the storage capacity without expanding the physical footprint. Warehouses employ different types of pallet racks, such as selective racks that allow direct access to each pallet, drive-in racks for last-in, first-out (LIFO) inventory rotation, and push-back racks that facilitate high-density storage. Each type is selected based on the specific storage requirements and inventory characteristics, ensuring a customized approach to space optimization.
Cantilever Racks: Ideal for Long, Bulky, and Irregularly Shaped Items
Cantilever racks are specially designed for the storage of long, bulky, or irregularly shaped items that cannot be accommodated on traditional shelving units. These racks feature arms extending from vertical columns, providing unobstructed storage space for items such as lumber, pipes, or furniture. Cantilever racks offer adjustable arms, allowing warehouses to customize the storage configuration based on the dimensions of the stored items. This flexibility ensures efficient utilization of space while accommodating items of varying sizes and shapes. By eliminating the need for aisles between shelves, cantilever racks maximize storage density and provide easy accessibility to stored items, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Drive-In Racks: Optimizing Storage through Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) Rotation
Drive-in racks are a specialized storage solution designed to optimize storage density by employing the last-in, first-out (LIFO) inventory rotation method. These racks consist of multiple lanes with rails for pallet placement, allowing forklifts to drive directly into the rack structure. When a new pallet is added, it pushes existing pallets further into the rack. During retrieval, the last pallet added becomes the first to be removed, ensuring efficient use of space and rotation of inventory. Drive-in racks are particularly suitable for items with a long shelf life or those requiring bulk storage. By eliminating the need for aisles between racks, this storage solution maximizes warehouse space, making it ideal for warehouses dealing with large quantities of homogeneous products.
Labour Management
In the intricate dance of warehouse operations, the human element remains indispensable. A knowledgeable and motivated workforce forms the backbone of efficient warehouse management. Training programs, performance metrics, and technology-driven solutions empower employees to handle diverse tasks effectively, contributing to the overall success of warehouse operations.
Consider the workforce as the backbone, providing essential support to every aspect of warehouse functionality. A knowledgeable and motivated team ensures that the intricate dance of operations flows smoothly. In this mechanism, each employee is not just a participant but a key contributor to the overall success of the warehouse.
To enhance the capabilities of the workforce, warehouses invest in comprehensive training programs. These programs equip employees with the essential skills and knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of modern warehouse operations. From operating machinery to understanding safety protocols, training ensures that every team member is proficient and confident in their role.
Performance metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) step onto the stage to monitor employee productivity. These metrics are like the scorecards in our symphony, keeping track of key aspects such as order picking speed, accuracy rates, and order fulfillment times. Real-time monitoring provides valuable insights, allowing managers to identify areas for improvement and implement targeted training initiatives. This creates a healthy competition among employees, motivating them to achieve and exceed established benchmarks.
Training Programs
Training programs are pivotal in equipping warehouse staff with the necessary skills and knowledge to navigate the complexities of modern warehouse operations. Proper training ensures employees are proficient in operating machinery, understanding safety protocols, and following efficient workflows. Training modules cover a wide range of topics, including forklift operation, inventory management software, safety procedures, and customer service skills. By investing in comprehensive training, warehouses create a skilled workforce capable of handling various tasks with precision and confidence. Well-trained employees contribute to enhanced productivity, reduced errors, and increased operational efficiency, making training programs a cornerstone of successful labor management.
Performance Metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Effective labor management relies on the implementation of performance metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to monitor employee productivity and assess overall warehouse performance. By establishing clear KPIs, managers can track key aspects such as order picking speed, accuracy rates, inventory turnover, and order fulfillment times. Real-time monitoring of KPIs provides valuable insights into individual and team performance, enabling managers to identify areas for improvement and implement targeted training initiatives. Performance metrics foster healthy competition among employees, encouraging them to achieve and exceed established benchmarks. By aligning individual goals with organizational objectives, warehouses create a motivated workforce committed to maintaining high productivity levels, ensuring seamless operations, and meeting customer demands with efficiency and accuracy.
Automation and Robotics
The integration of automation and robotics has ushered in a new era of labor optimization within warehouses. Automation technologies, such as Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and robotic arms, handle repetitive tasks and streamline various operations, allowing human resources to focus on complex and strategic activities.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are autonomous, self-guided vehicles equipped with sensors and control systems that allow them to navigate warehouses without human intervention. These vehicles follow predetermined paths, transporting goods between locations, such as storage areas, picking stations, and shipping docks. AGVs optimize material flow within the warehouse, eliminating the need for manual labour in tasks such as material handling and transportation. By reducing reliance on manual equipment, AGVs enhance operational efficiency, minimize errors, and contribute to a safer work environment. AGVs are particularly valuable in large warehouses dealing with high volumes of products, where their precision and speed significantly improve overall logistics and inventory management.
Robotic Arms
Robotic arms, also known as industrial robots, are programmable mechanical devices designed to perform a wide range of tasks with precision and speed. In warehouse operations, robotic arms are employed in tasks such as picking, packing, stacking, and palletizing. These robots use advanced sensors and algorithms to identify, grasp, and manipulate items of varying shapes, sizes, and weights. By automating repetitive tasks, robotic arms significantly enhance the speed and accuracy of warehouse operations. These robots work collaboratively with human employees, augmenting their capabilities and enabling the efficient handling of diverse products. Robotic arms are particularly beneficial in e-commerce fulfillment centers, where rapid order processing and precise packing are essential to meet customer expectations. By integrating robotic arms into the workforce, warehouses achieve higher throughput, reduce order fulfillment times, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Conveyor Systems
Conveyor systems are integral components of modern warehouses, streamlining the movement of goods within the facility. These systems consist of motorized belts, rollers, or chains that transport items from one location to another, eliminating the need for manual handling and reducing labor-intensive tasks. Conveyor belts are strategically installed throughout the warehouse, connecting various stages of the order fulfillment process, such as picking, packing, sorting, and shipping. As items move along the conveyor, employees can focus on specific tasks, such as quality checks, labeling, or packaging, maximizing their productivity and efficiency. Conveyor systems are highly versatile and can be customized to accommodate different product sizes and weights, making them suitable for a wide range of industries, including retail, manufacturing, and distribution. By automating material handling, conveyor systems enhance operational flow, minimize errors, and contribute to a more efficient and organized warehouse environment.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
In the digital age, Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) have emerged as indispensable tools for optimizing warehouse operations. Operating behind the scenes, these dynamic facilities engage in all the processes, serving as the connector in the supply chain. Their significance extends beyond mere storage, evolving into sophisticated centers where technology, logistics, and human expertise converge.
The surge in demand for diverse products has propelled warehouses into strategic roles, necessitating an intricate coordination among various elements. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) have emerged as transformative tools in this landscape, revolutionizing the traditional approaches to inventory control, order fulfillment, and overall warehouse orchestration. More than just software, WMS represents a digital evolution, introducing a new era of efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability in warehouse operations.
As we delve into the core elements of effective warehouse management, the spotlight is on WMS, unraveling its significance in offering real-time visibility, enhancing accuracy, and ultimately contributing to the competitive edge of businesses in the modern marketplace. Join us in this exploration, where the synergy of technology and warehouse dynamics takes center stage, reshaping the narrative of efficient and effective supply chain management.
Enhanced Visibility – Real-time Insights for Informed Decisions
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) provides a comprehensive overview of warehouse operations, offering real-time insights into inventory levels, order statuses, and employee productivity. Managers can access critical data, empowering them to make informed decisions and proactively address operational challenges. Real-time visibility enables managers to identify bottlenecks, monitor stock levels, and optimize workflows, ensuring seamless operations. By staying updated on key metrics, managers can implement strategic interventions, reducing delays, errors, and costs. Enhanced visibility also fosters collaboration among team members, allowing for effective communication and coordination in response to changing market demands. Ultimately, real-time insights provided by WMS enable warehouses to maintain agility and responsiveness, catering to customer needs with precision and efficiency.
Improved Accuracy – Minimizing Errors through Automation
Accuracy is paramount in warehouse management, where errors can lead to costly mistakes, dissatisfied customers, and damaged reputations. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) automate various processes, reducing the likelihood of human errors in tasks such as order processing, picking, packing, and shipping. Automated barcode scanning and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technologies enhance accuracy by ensuring that the right products are picked, packed, and shipped to the correct customers. Barcode scanning enables employees to scan product codes, verifying item accuracy and reducing the risk of misplacements. RFID technology, on the other hand, uses radio waves to identify and track products, allowing for real-time monitoring of inventory movement. By leveraging these technologies, WMS minimizes errors, enhancing order accuracy and customer satisfaction. Accurate order fulfillment builds trust with customers, fostering loyalty and repeat business, reinforcing the importance of automation in ensuring precision within warehouse operations.
Increased Efficiency
Efficiency lies at the heart of successful warehouse management, where streamlined processes translate into reduced lead times, increased throughput, and higher customer satisfaction. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) play a pivotal role in optimizing efficiency by automating tasks such as order prioritization, route optimization, and inventory management. WMS evaluates various factors, including product availability, order urgency, and shipping methods, to prioritize orders and allocate resources effectively. By automating these decisions, WMS minimizes idle time, ensures optimal use of resources, and maximizes throughput. WMS also optimizes inventory management by implementing techniques such as cross-docking, where products are directly transferred from receiving to shipping, bypassing storage. By reducing storage time and handling, cross-docking enhances order fulfillment speed and reduces operational costs. Additionally, WMS automates inventory replenishment, ensuring that stock levels are maintained at optimal levels, minimizing stockouts, and preventing excess inventory. By streamlining these processes, WMS enhances operational efficiency, allowing warehouses to handle higher volumes of orders and improve overall profitability.
Benefits of Warehouse Management Systems
Warehouse management brings forth a myriad of benefits for businesses, playing a pivotal role in enhancing overall operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Here are some key advantage
Optimized Inventory Levels
Efficient warehouse management goes beyond the simple storage of goods; it involves precise control of inventory levels. By employing advanced inventory management strategies like Just-In-Time (JIT) systems, businesses can minimize excess stock, preventing capital tie-up and reducing holding costs. Simultaneously, these strategies ensure that products arrive precisely when needed, avoiding stock outs, dissatisfied customers, and missed business opportunities.
Improved Order Fulfillment
Order fulfillment is the heartbeat of warehouse operations, requiring accurate picking, packing, and shipping. Techniques like batch picking, zone picking, and wave picking revolutionize the order fulfillment process. Batch picking optimizes routes and minimizes travel time, zone picking reduces congestion, and wave picking enables simultaneous handling of multiple orders. These strategies significantly enhance operational efficiency, contributing to faster and more accurate order fulfillment.
Enhanced Space Utilization
The strategic organization of products within a warehouse directly impacts storage capacity, accessibility, and operational flow. Various storage solutions, such as pallet racks, cantilever racks, and drive-in racks, optimize vertical space and accommodate items of different shapes and sizes. Efficient space utilization minimizes the physical footprint of the warehouse while maximizing storage capacity, a critical factor in maintaining a streamlined and cost-effective operation.
Real-time Visibility
Warehouse management systems (WMS) provide real-time insights into inventory levels, order statuses, and overall warehouse performance. This visibility is crucial for making informed decisions promptly. By staying updated on key metrics, businesses can identify bottlenecks, monitor stock levels, and optimize workflows, ensuring seamless operations and quick responses to market demands.
Accurate Data and Reporting
Warehouse management systems generate accurate data and comprehensive reports, offering valuable insights for performance analysis and decision-making. These reports cover various aspects, including order picking speed, accuracy rates, inventory turnover, and order fulfillment times. Accurate data facilitates informed decision-making, aiding in the identification of areas for improvement and the implementation of targeted training initiatives.
Agility and Adaptability
In the dynamic business environment, the ability to adapt swiftly to market fluctuations, changing customer demands, and unforeseen challenges is paramount. An efficiently managed warehouse, with agile and flexible processes, ensures that businesses can adjust operations promptly, maintaining competitiveness and meeting customer expectations.
Customer Satisfaction
Timely and accurate order fulfillment, coupled with effective inventory management, directly contributes to increased customer satisfaction. Beyond just delivering products, a well-managed warehouse contributes to positive brand experiences, fostering customer loyalty and encouraging repeat business.
Compliance and Quality Control
Warehouse management processes often include checks for compliance with industry regulations and quality control measures. By ensuring that products meet standards and regulations, businesses prevent costly errors, maintain a positive brand image, and comply with legal requirements, contributing to long-term success.
Scalability
As businesses grow, a well-organized warehouse can easily scale operations. Whether handling increased order volumes or expanding the product range, scalability ensures that efficiency and effectiveness are maintained, allowing businesses to grow sustainably.
Conclusion
In the vast world of commerce, warehouses emerge not merely as storage spaces but as orchestrators of precision and efficiency. This exploration into warehouse management reveals a complex operation, far beyond handling inventory. Warehouses, acting as logistical nerve centers, ensure secure, organized, and precise product movement from manufacturing plants to consumers.
Global market demands have elevated warehouses into strategic hubs where technology, human expertise, and logistics seamlessly converge. Our deep dive into key management elements highlights inventory control, order fulfillment, space optimization, and labor management.
The introduction of advanced Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) marks a new era in operational efficiency. These digital supply chain solutions provide real-time visibility, offering businesses a competitive edge. With enhanced accuracy, streamlined processes, and a pulse on performance, WMS exemplifies the technological evolution in modern warehousing.
In essence, warehouses aren’t just physical; they are dynamic, data-driven entities crucial to global trade. Their precise operations and embrace of technology underscore their pivotal role in the supply chain. As we conclude this exploration, mastering warehousing goes beyond storage—it’s about mastering the art of seamless, efficient, and customer-centric operations. Those navigating this landscape, leveraging technology and refining processes, aren’t just participants; they are architects shaping the future of commerce through warehousing excellence.
FAQs
A WMS is a software solution designed to optimize warehouse operations, including inventory tracking, order processing, and supply chain management.
Choosing the right WMS streamlines operations, reduces errors, improves efficiency, and supports your business’s growth and strategic goals.
Start by evaluating your current warehouse processes, identifying pain points like inventory inaccuracies or slow order processing, and defining the features you require.
Look for real-time inventory management, seamless ERP/CRM integration, scalability, user-friendly interface, advanced reporting, and customization options.
Customization ensures the WMS fits your unique business workflows and adapts as your needs evolve, maximizing long-term effectiveness.
People also read:
- Demand-driven Replenishment Practices for Retailers
- Guide to Managing Perishable Inventory
- What Is a Bill of Materials (BOM)? Expert Guide & Tips
- Inventory Management with Barcode Technology
- Common Inventory Management Challenges

Kapil Pathak is a Senior Digital Marketing Executive with over four years of experience specializing in the logistics and supply chain industry. His expertise spans digital strategy, search engine optimization (SEO), search engine marketing (SEM), and multi-channel campaign management. He has a proven track record of developing initiatives that increase brand visibility, generate qualified leads, and drive growth for D2C & B2B technology companies.