In today’s fast-paced world of logistics, efficiency and accuracy are non-negotiable. Companies are turning to innovative technologies like QR codes to optimize inventory management and warehouse operations. QR codes, short for Quick Response codes, are two-dimensional barcodes capable of storing vast amounts of data. Originally developed by Denso Wave in Japan for tracking car parts, these codes have evolved into a vital tool for businesses across industries.

QR codes play a crucial role in improving accuracy, reducing errors, and enabling real-time inventory tracking in warehouses. Their adoption in logistics has grown exponentially due to their affordability, ease of implementation, and compatibility with existing systems. This article delves into the components, benefits, challenges, and future potential of QR code technology in inventory management and warehouse operations.
How QR Codes Work in Warehouse Operations
Components of a QR Code System
A typical QR code system for warehouse operations includes three primary components:
- QR Code Labels: Unique codes affixed to products, pallets, or bins.
- QR Code Scanners: Devices (or mobile apps) used to read and decode the information stored in the QR code.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Software that integrates QR code data into inventory management workflows.
Scanning and Decoding: Understanding the Process
When a QR code is scanned, the encoded information—such as product ID, batch number, or location—is instantly decoded and transmitted to the WMS. This real-time transfer ensures that inventory updates are immediate, reducing the risk of human errors.
Integration with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
QR codes seamlessly integrate with cloud WMS platforms, enabling automated tracking of goods. Whether it’s inbound, outbound, or in-warehouse movements, every step is logged digitally, providing managers with actionable insights.
Benefits of Using QR Codes for Inventory Management
1. Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors
Manual data entry is prone to errors, but QR codes automate the process, ensuring precise inventory tracking. This reduces discrepancies and improves overall operational accuracy.
2. Faster Processing Speeds
Unlike traditional barcodes, QR codes can be scanned from any angle, speeding up inventory checks and reducing processing times.
3. Improved Real-Time Inventory Tracking
QR codes enable real-time updates to the WMS, allowing managers to track stock levels instantly and make informed decisions.
4. Cost-Effective Solution Compared to Alternatives
Compared to RFID technology, QR codes are significantly more affordable, making them an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
5. Scalability and Versatility
QR codes can be easily scaled to accommodate growing warehouses and diversified inventory, making them a future-proof solution.
6. Environmentally Friendly Option
Using QR codes on digital platforms eliminates the need for paper-based records, contributing to sustainability goals.
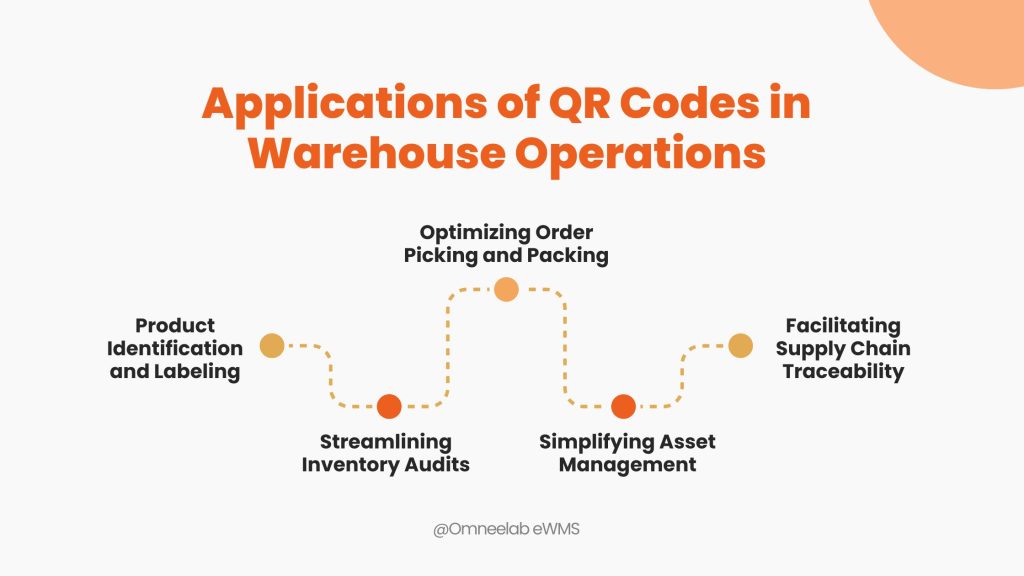
Applications of QR Codes in Warehouse Operations
Product Identification and Labeling
QR codes provide detailed product information, such as manufacturing dates, batch numbers, and storage conditions. This simplifies the process of locating and identifying items.
Streamlining Inventory Audits
With QR codes, warehouse audits become a breeze. Scanning codes during audits ensures that inventory records are accurate and up-to-date.
Optimizing Order Picking and Packing
By scanning QR codes, workers can quickly locate items for orders, reducing picking errors and improving customer satisfaction.
Simplifying Asset Management
QR codes are not limited to products; they are also used for tracking warehouse equipment and assets, ensuring proper maintenance schedules.
Facilitating Supply Chain Traceability
QR codes can track goods across the entire supply chain, ensuring transparency and accountability in logistics.
Challenges in Implementing QR Codes for Warehousing
Initial Setup Costs
Although QR codes are cost-effective in the long run, the initial setup—purchasing printers, scanners, and integrating software—can be a financial hurdle for small businesses.
Training Workforce to Use QR Systems
Employees need training to effectively use QR code systems, which can temporarily disrupt operations during the transition phase.
Ensuring Equipment Compatibility
Older warehouse equipment might not be compatible with QR code scanners or the software needed for integration.
Data Security Concerns
Storing sensitive inventory data within QR codes raises security issues, requiring robust encryption and secure systems.
Durability of QR Code Labels
QR code labels must withstand harsh warehouse conditions, such as extreme temperatures, moisture, and abrasion, to remain functional.
How to Implement QR Codes for Inventory Management
Planning and Choosing the Right Tools
Define your goals and assess your warehouse needs before selecting QR code printers, scanners, and compatible WMS software.
Integrating QR Codes with Existing Software
Ensure that your chosen system integrates seamlessly with your current operations to avoid workflow disruptions.
Testing and Training
Conduct pilot tests and train employees to ensure smooth adoption of the new system.
Scaling the Implementation
Once tested successfully, scale the QR code system to cover all warehouse operations, from inventory receiving to order fulfillment.
Comparing QR Codes with Other Technologies
QR Codes vs. Barcodes: Which is Better?
While barcodes are simpler, QR codes store more data and offer greater versatility in warehouse operations.
QR Codes vs. RFID for Inventory Management
Although RFID enables remote tracking without direct line-of-sight, QR codes are more cost-effective and easier to implement.
QR Codes vs. NFC Technology
Near Field Communication (NFC) tags are gaining popularity, but QR codes remain a more accessible and scalable solution for inventory management.
Future Trends in QR Code Technology for Warehousing
AI-Driven QR Code Systems
Artificial Intelligence is being integrated into QR code systems to predict inventory needs and optimize stock levels.
QR Codes for Predictive Analytics in Warehousing
QR codes provide data that, when analyzed, can forecast demand trends, helping businesses prepare for future challenges.
Integration with IoT and Blockchain Technology
QR codes are increasingly linked with IoT devices and blockchain, enhancing transparency and traceability in supply chains.
Dynamic QR Codes for Real-Time Updates
Dynamic QR codes can be updated with new information without needing to reprint labels, offering flexibility and reducing waste.
Conclusion
QR codes have emerged as a transformative technology for inventory management and warehouse operations. Their ability to store and share information in real time, coupled with their affordability, makes them an invaluable asset for businesses aiming to optimize logistics. By adopting QR codes, companies can enhance accuracy, streamline workflows, and improve overall efficiency. As technology evolves, QR codes will continue to play a pivotal role in driving transparency, accuracy, and sustainability in warehousing.
FAQs on QR Codes for Inventory Management
1. What is the cost of implementing QR codes in warehouses?
Costs vary based on the size of the warehouse and the complexity of the system, but QR codes remain affordable compared to RFID.
2. Can QR codes work with existing inventory systems?
Yes, QR codes can be integrated with most modern WMS platforms for seamless operation.
3. How secure is QR code technology for inventory data?
With proper encryption and secure WMS, QR Code for Inventory Management are safe.
4. What industries benefit the most from QR code systems?
Industries like retail, e-commerce, manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals see the most benefit.
5. How do QR codes compare with RFID for small-scale operations?
For small businesses, QR Code for Inventory Management are a cost-effective alternative to RFID.
6. Is QR code technology scalable for large warehouses?
Yes, QR code systems can be easily scaled to accommodate larger operations.

Kapil Pathak is a Senior Digital Marketing Executive with over four years of experience specializing in the logistics and supply chain industry. His expertise spans digital strategy, search engine optimization (SEO), search engine marketing (SEM), and multi-channel campaign management. He has a proven track record of developing initiatives that increase brand visibility, generate qualified leads, and drive growth for D2C & B2B technology companies.